Plant biotechnology has revolutionized how scientists propagate and conserve plant species. Among the most remarkable advancements are somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seed technology, which together make it possible to clone plants efficiently, conserve rare species, and develop uniform elite lines for agriculture and research. These methods rely on one fundamental biological concept, totipotency, the ability of a single plant cell to regenerate into a complete organism.

This property forms the foundation of plant tissue culture, allowing scientists to produce true-to-type plants, rescue hybrids, and multiply rare germplasm.

- Induction : Callus tissue or explants are cultured on a medium rich in auxins (like 2,4-D), which stimulates cells to become embryogenic.
- Embryoid Formation : Embryogenic cells organize into structures resembling zygotic embryos, these are called embryoids. They possess shoot and root poles but lack endosperm.
- Maturation : Embryoids mature in the presence of reduced auxin and increased cytokinin concentrations.
- Germination : Mature somatic embryos are transferred to hormone-free media, where they germinate into plantlets.
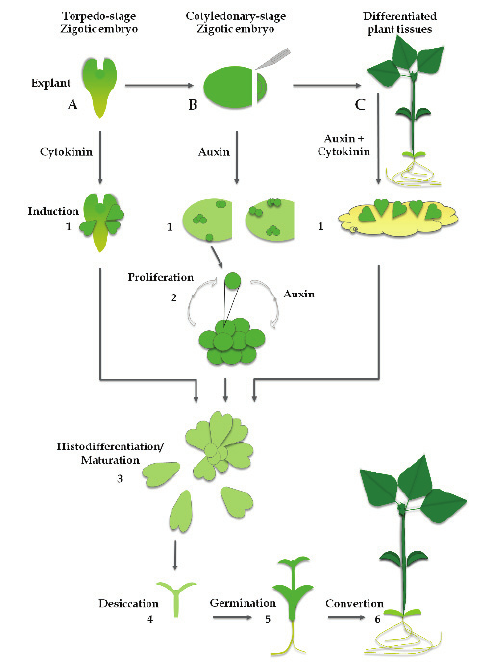
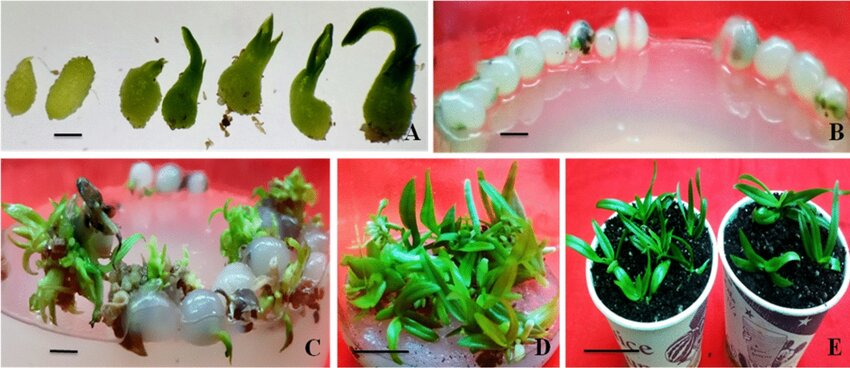
- Somatic embryos are coated with a gel matrix (commonly sodium alginate and calcium chloride) to form protective capsules.
- The capsule provides physical protection, nutrient supply, and moisture retention.
- Nutrient additives (sucrose, vitamins, and growth regulators) enhance embryo survival.
- Embryo maturity
- Composition of the encapsulation matrix
- Storage duration and temperature
Once the synthetic seed germinates, the resulting plantlet undergoes acclimatization to greenhouse or field conditions.
🧫 Cryopreservation : Encapsulated embryos can be stored at ultra-low temperatures for years.
Somatic embryogenesis and synthetic seed technology showcase how deeply plant biotechnology can harness cellular potential. Through the concept of totipotency, even a single cell can regenerate an entire plant transforming both basic research and commercial propagation systems. These innovations pave the way for sustainable agriculture, genetic conservation, and large-scale production of elite cultivars.